Organised Trading Facilities (OTF) in Financial Markets
Introduction
According to the definition provided by Market Investopedia, an organised trading facility (OTF) is a trading venue that enables the buying and selling of various financial securities, such as bonds and structured finance products. When compared to regulated markets and multilateral trading facilities (MTFs), an open-market trading facility (OTF) operates under a framework that is more flexible, while yet maintaining transparency and fairness in the transactions that take place. Within the framework of the MiFID II regulations, open-ended funds (OTFs) play a significant part in permitting transactions that allow a party to acquire and sell interests in financial instruments to function in an effective manner.
What is an Organised Trading Facility (OTF)?
Trading platforms that allow for the matching of buying and selling interests in a discretionary manner are referred to as organised trading facilities. The fact that it enables trading based on negotiations, in particular with regard to bonds and structured finance product emissions, sets it apart from conventional trading venues such as stock exchanges and MTFs. Understanding forex sentiments in these markets helps traders assess market dynamics and make informed decisions when engaging in discretionary trading.
Functions and Characteristics of Organised Trading Facilities
- Flexibility in Trading: Unlike regulated markets, OTFs allow discretionary execution of orders.
- Focus on Bonds and Structured Finance Products: OTFs facilitate trading in bonds, derivatives, and other non-equity instruments.
- Regulated under MiFID II: The European Union’s MiFID II framework ensures transparency and fair practices in OTF operations.
- Multilateral Trading: These platforms involve multiple participants buying and selling interests in financial instruments.

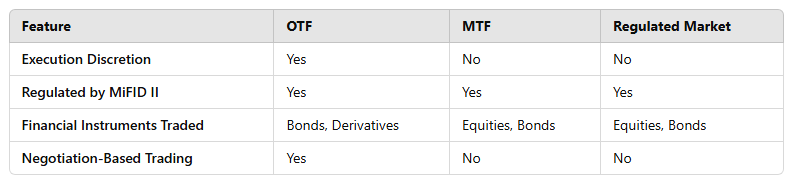
Difference Between OTF, MTFs, and Regulated Markets
Under defined listing and trading guidelines, a regulated market runs under clear disclosure requirements for issuers. On the other hand, an OTF offers a more flexible trading environment that fits several financial instruments including bonds and structured finance products. As long as all market players can follow the same rules, a multilateral trading facility (MTFs) is the same thing as an OTF: it’s a place where people can trade.
The Role of MiFID II in OTF Regulation
In order to promote investor protection, fairness, and openness, the European Union has implemented MiFID II, which regulates exchange traded funds (OTFs). In order to avoid market manipulation and maintain compliance with financial rules, the framework imposes stringent reporting obligations on operators of open-ended trading funds (OTF operations).
Advantages of Trading on an Organised Trading Facility
- Increased Market Transparency: OTFs operate under MiFID II, ensuring transparent pricing and trade reporting.
- Flexibility in Order Execution: Traders benefit from negotiated trading, which allows better pricing and execution terms.
- Liquidity in Bond Markets: OTFs provide liquidity for bonds and structured finance product emissions, making them an essential part of financial markets.
- Regulatory Oversight: Unlike over-the-counter (OTC) trading, OTFs adhere to strict regulations to protect investors.
Challenges of Organised Trading Facilities
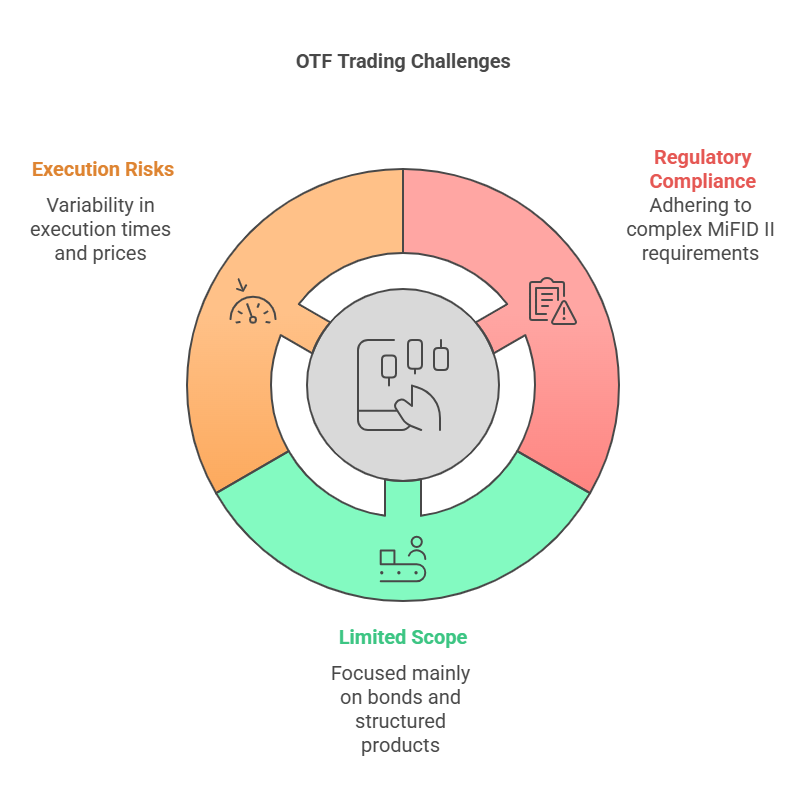
- Regulatory Compliance: Operators must adhere to MiFID II requirements, which can be complex.
- Limited Scope: Unlike stock exchanges, OTFs mainly deal with bonds and structured finance products.
- Execution Risks: Since trading is discretionary, execution times and prices may vary.
Final Thoughts
Following the restrictions of MiFID II, an organised trading facility (OTF) is an essential trading venue for structured finance instruments and bonds. It offers both transparency and flexibility to the market participants. In order to ensure that market participants are able to engage in trading that is both efficient and effective, an OTF, which utilises a discretionary execution model, acts as a vital platform for financial instruments.
FAQ
This addresses the fundamental definition and purpose of an OTF.
This clarifies the distinctions between different types of trading venues.
This focuses on the specific assets, such as bonds and structured finance products, that are commonly traded.
This directly addresses a common instrument traded on these platforms.
